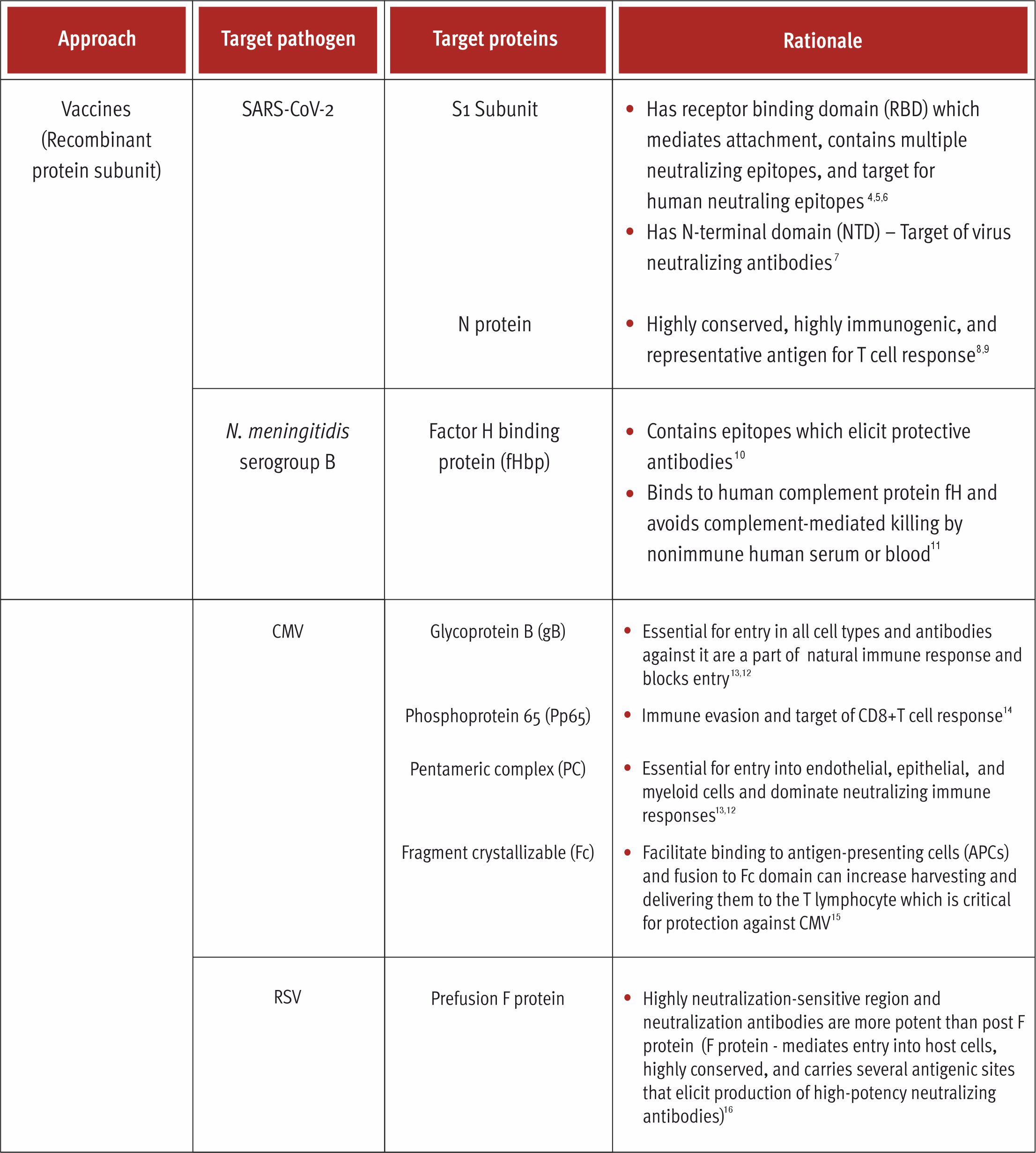
Recombinant Protein Subunits
Recombinant protein vaccines are subunit vaccines that utilize only a small part of the pathogen and elicit immune response against few protective antigens.1 These vaccines are composed of antigenic viral proteins that can be expressed in heterologous expression systems.2,3 A wide range of expression systems are used for expressing these proteins such as Escherichia coli, mammalian cells, yeast, etc.2,3 This ensures that the antigen has a well-defined composition, no risk of pathogenicity in its use and the antigen synthesis and purification can be scaled up in cost-effective manner.2,3 Since proteins cannot replicate, the side effects with these vaccines are negligible.1 These vaccines are more secured than live attenuated and inactivated killed vaccines.3 In the past 3 decades, there has been a trend towards developing these subunit vaccines formulated using specific antigenic proteins with suitable potent adjuvants.3
References :
- Matić Z, Šantak M. Current view on novel vaccine technologies to combat human infectious diseases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;106(1):25-56. doi:10.1007/s00253-021-11713-0
- Bill RM. Recombinant protein subunit vaccine synthesis in microbes: a role for yeast?. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;67(3):319-328. doi:10.1111/jphp.12353.
- Wang M, Jiang S, Wang Y. Recent advances in the production of recombinant subunit vaccines in Pichia pastoris. Bioengineered. 2016;7(3):155-165. doi:10.1080/21655979.2016.1191707.
- Naqvi AAT, Fatima K, Mohammad T, et al. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(10):165878. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165878.
- Yu F, Xiang R, Deng X, et al. Receptor-binding domain-specifi human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Signal Transduct TargetTher. 2020;5{1):212. Published 2020 Sep 22. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00318-o.
- Liu Z, Xu W, Xia S, et al. RBD-Fc-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate induces highly potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody response. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5{1):282. Published 2020 Nov 27. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00402-5.
- Dai L, Gao GF. Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19. Nat Rev lmmunol. 2021;21(2):73-82. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00480-o.
- Zhang J, Zeng H, Gu J, Li H, Zheng L, Zou Q. Progress and Prospects on Vaccine Development against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines (Basel). 2020;8(2):153. Published 2020 Mar 29. doi:10.3390/vaccines8020153.
- Dutta NK, Mazumdar K, Gordy JT. The Nucleocapsid Protein ofSARS-CoV-2: a Target for Vaccine Development. J Virol. 2020;94(13):eoo647-20. Published 2020 Jun 16. doi:10.1128/JVl.00647-20.
- Rivero-Calle I, Raguindin PF, Gomez-Rial J, Rodriguez-Tenreiro C, Martinon-Torres F. Meningococcal Group B Vaccine For The Prevention Of Invasive Meningococcal Disease Caused By Neisseria meningitidis Serogroup B. Infect Drug Resist. 2019;12:3169-3188. Published 2019 Oct 9.doi:10.2147/DR.S159952.
- Granoff M. Review of meningococcal group B vaccines. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50 Suppl 2(S2):S54-S65. doi:10.1086/648966.
- Sandonfs V, Garcfa-Rfos E, McConnell MJ, Perez-Romero P. Role of Neutralizing Antibodies in CMV Infection: Implications for New Therapeutic Approaches. Trends Microbiol. 2020;28(11):900-912. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2020.04.003.
- McVoy MM, Tenorio E, Kauvar LM. A Native Human Monoclonal Antibody Targeting HCMV gB (AD-2 Site I). Int J Mal Sci. 2018;19(12):3982. Published 2018 Dec 11. doi:10.3390/ijms19123982.
- Hyun SJ, Sohn HJ, Lee HJ, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Cytomegalovirus pp65 Antigen-Specifi CD8+ T Cell Responses According to Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Allotypes and lntraindividual Dominance. Front lmmunol. 2017;8:1591. Published 2017 Nov 21. doi:10.3389/fimmu.207.01591.
- Tabaei S, Mashkani B, Esmaili A, Karimi R, Jamehdar SA. Design of cocktail peptide vaccine against Cytomegalovirus infection. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016;19(4): 449-454.
- Mejias A, Rodrfguez-Fernandez R, Oliva S, Peeples ME, Ramilo 0. The journey to a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Ann Allergy Asthma lmmunol. 2020;125(1): 36-46. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2020.03.017.
