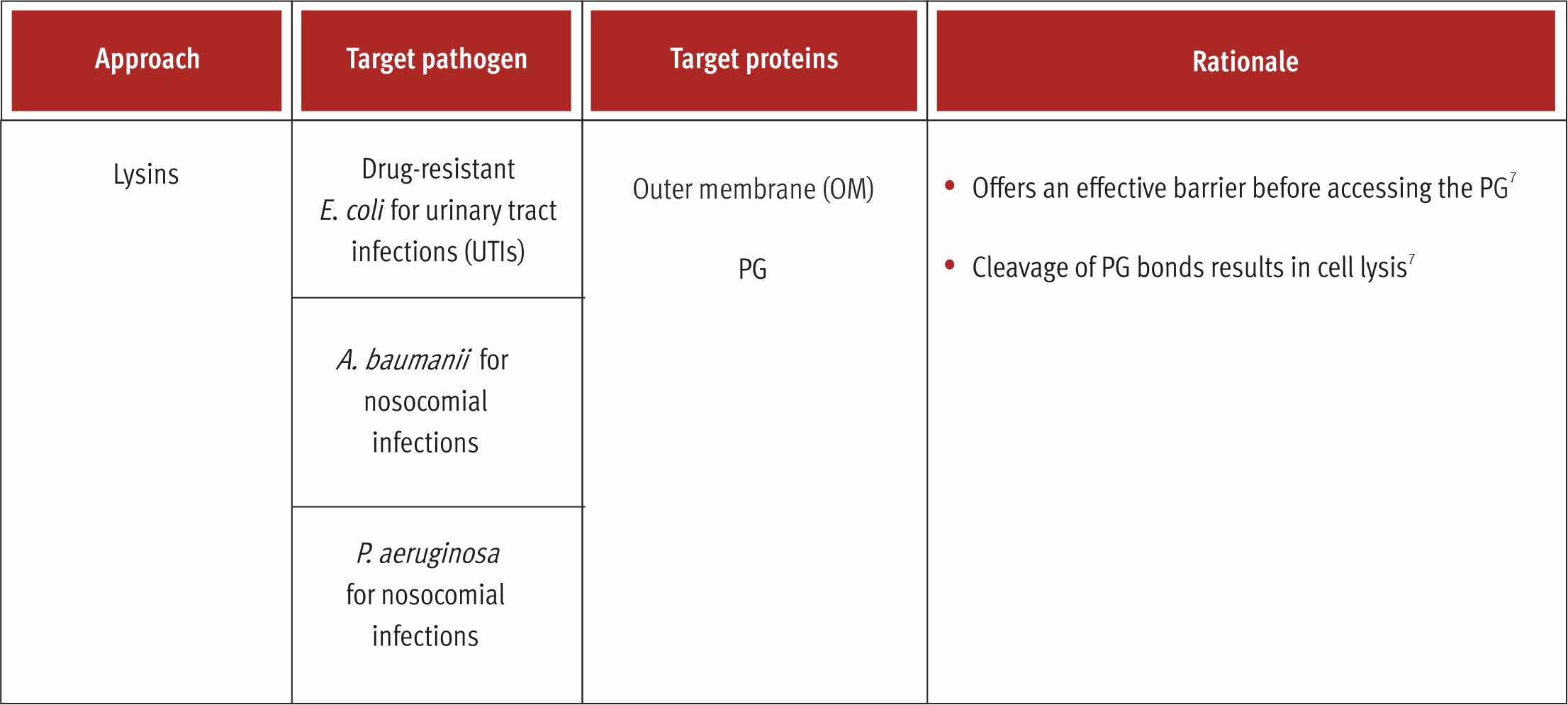
Lysins
Bacteriophage-derived proteins such as endolysins provide a robust solution to put a lid on the AMR menace. Although phages have long been used for the treating bacterial infections, the use of endolysins is relatively new.3 These phage lysins represents one of the most advanced classes of antibacterials under clinical investigations having a novel mode of action based on peptidoglycan (PG) degradation.1 Lysins when applied exogenously (as purified recombinant proteins) to Gram-positive bacteria, bring about rapid lysis and death of the bacterial cell.4 Considerable progress has been made in evaluating lysins with Gram-negative bacterial activity, with researchers identifying naturally occurring Gram-negative lysins that work from outside to bioengineering lysins by fusing bacterial cell surface binding proteins to lysin catalytic domains, and combining lysins with outer membrane permeabilizing agents.5 The modular structure of lysins makes it possible to design bioengineered lysins that have desired properties viz. high activity, broader killing spectrum, and effective against Gram-negative bacteria.6 Lysins possess exhibit several advantages over antibiotics highlighted by Vasquez et al.2 Due to the numerous features, endolysins have been assigned to a new class of antimicrobial agents termed as enzybiotics”.3
References:
- Gutierrez D, Briers Y. Lysins breaking down the walls of Gram-negative bacteria, no longer a no-go. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021;68:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio. 2020.08.014.
- Vazquez R, Garcfa E, Ga ref a P. Phage Lysins for Fighting Bacterial Respiratory Infections: A New Generation of Antimicrobials. Front lmmunol. 2018;9:2252. Published 2018 Oct 16. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.2252.
- Murray E, Draper LA, Ross RP, Hill C. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Endolysins in a Clinical Setting. Viruses. 2021;13(4):680. Published 2021 Apr 15. doi:10.3390/v13040680
- Fenton M, Ross P, McAulife 0, O’Mahony J, CCoey A. Recombinant bacteriophage lysins as antibacterials. Bioeng Bugs. 2010;1(1):9-16. doi:10.4161/bbug.1.1.9818.
- Pastagia M, Schuch R, Fischetti VA, Huang DB. Lysins: the arrival of pathogen-directed anti-infectives.J Med Microbial. 2013;62(Pt 10):1506-1516. doi:10.1099 /jmm.0.061028-0.
- Yang Yu J, Wei H. Engineered bacteriophage lysins as novel anti-infectives. Front Microbial. 2014;5:542. Published 20140ct 16. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00542.
- Naqvi AAT, Fatima K, Mohammad T, et al. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(10):165878. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165878
